Bootstrap
This document describes how to bootstrap (install from scratch) the complete demo. This is separate from and in addition to the quickstart which describes a simplified setup and demo runthrough on a single cluster and the actual demo preparation and execution steps.
- Prerequisites
- Planning your installation
- Clone the manuela repository
- Fork and clone manuela-dev
- Create the gitops repository
- CI and Test (Mandatory)
- Factory Datacenter & Line Data Server (Mandatory)
- Optional extensions
Prerequisites
Logical Environments
This edge demo storyline spans multiple environments, from edge deployments over remote datacenters and central datacenters to public cloud environments. These logical environments can be mapped to a smaller number of physical environments. The following table gives an overview of the mapping in the stormshift environment:
| Logical Environment Name | Status | Namespaces | Stormshift Mapping | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development | Optional | iotdemo | ocp3 | Development environment, hosts e.g. AMQ Broker for IOT App Dev |
| CodeReady Workspaces | Optional | manuela-crw | ocp3 | Development on-demand |
| CI/CD & Test | Mandatory | manuela-ci, manuela-tst-all | ocp3 | All-in-one CI/CD and functional testing environment |
| Factory Datacenter | Mandatory | manuela-*-line-dashboard, manuela-*-messaging | ocp3 | Production environment in Factory |
| Line Data Server | Mandatory | manuela-*-machine-sensor | ocp4 | Production environment in Factory, close to production line |
| Central Datacenter | Mandatory | - | quay.io | Production environment in central datacenter, hosts enterprise registry |
| Management Cluster | Optional | manuela-nwpathoperator | ocp3 + pfSense VM | Cluster hosting the firewall operator which controls the firewall between Line Data Server and Factory Datacenter |
OpenShift clusters
Two or more OpenShift clusters version 4.3 or later are installed and running. You have administrative access to these clusters. The instructions assume you are logged into the correct OpenShift cluster depending on the logical environment mapping (see above) for your demo setup. See Planning your installation for more details.
Github account
The demo uses GitHub for the GitOps git workflow. You need a GitHub account that can access the chosen GitOps repository (see below) and have a Personal Access Token with “repo” permissions.
Quay instance
This demo uses quay as the central registry. This can be quay.io or quay enterprise.
Create the repositories:
- iot-consumer
- iot-frontend
- iot-anomaly-detection
- iot-software-sensor
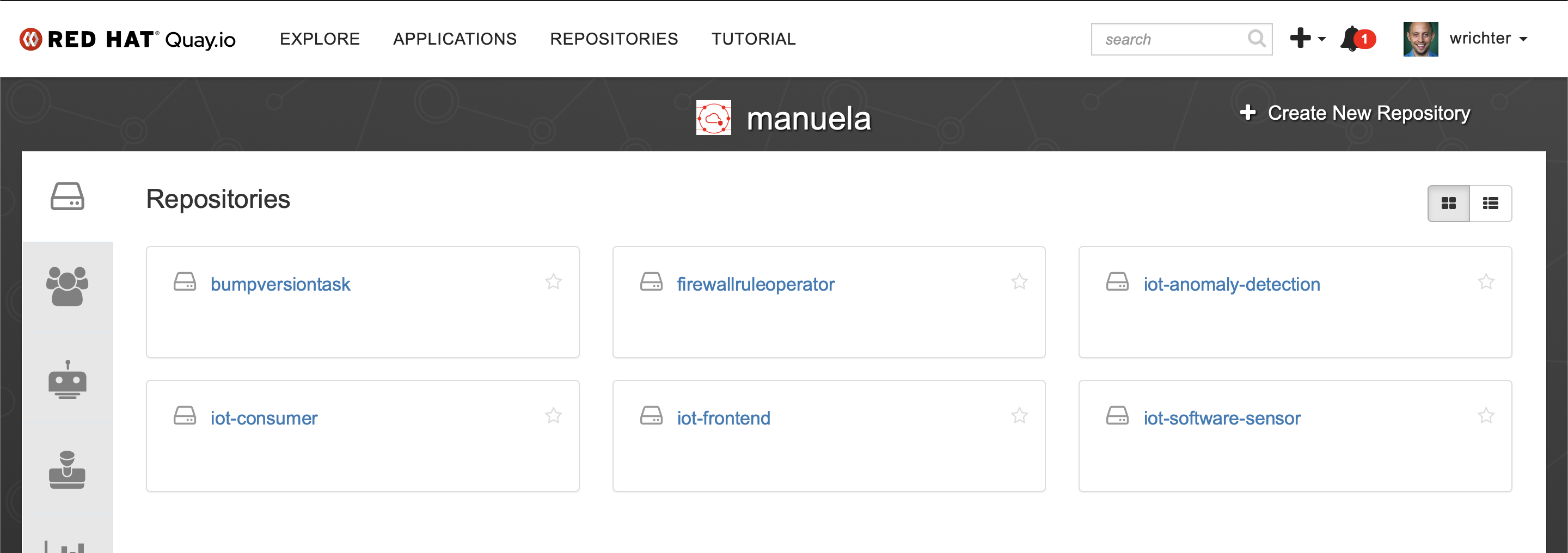
Also create a robot account “build”.
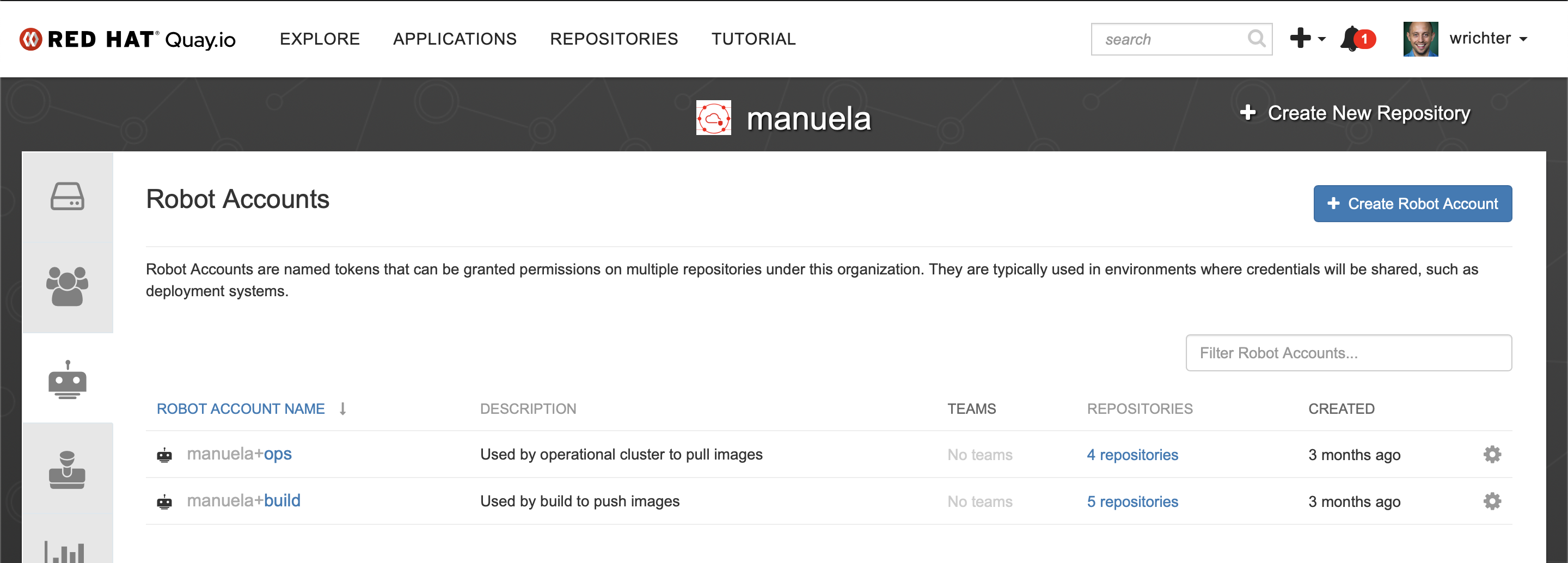
Ensure the robot account has write permissions to the repositories.
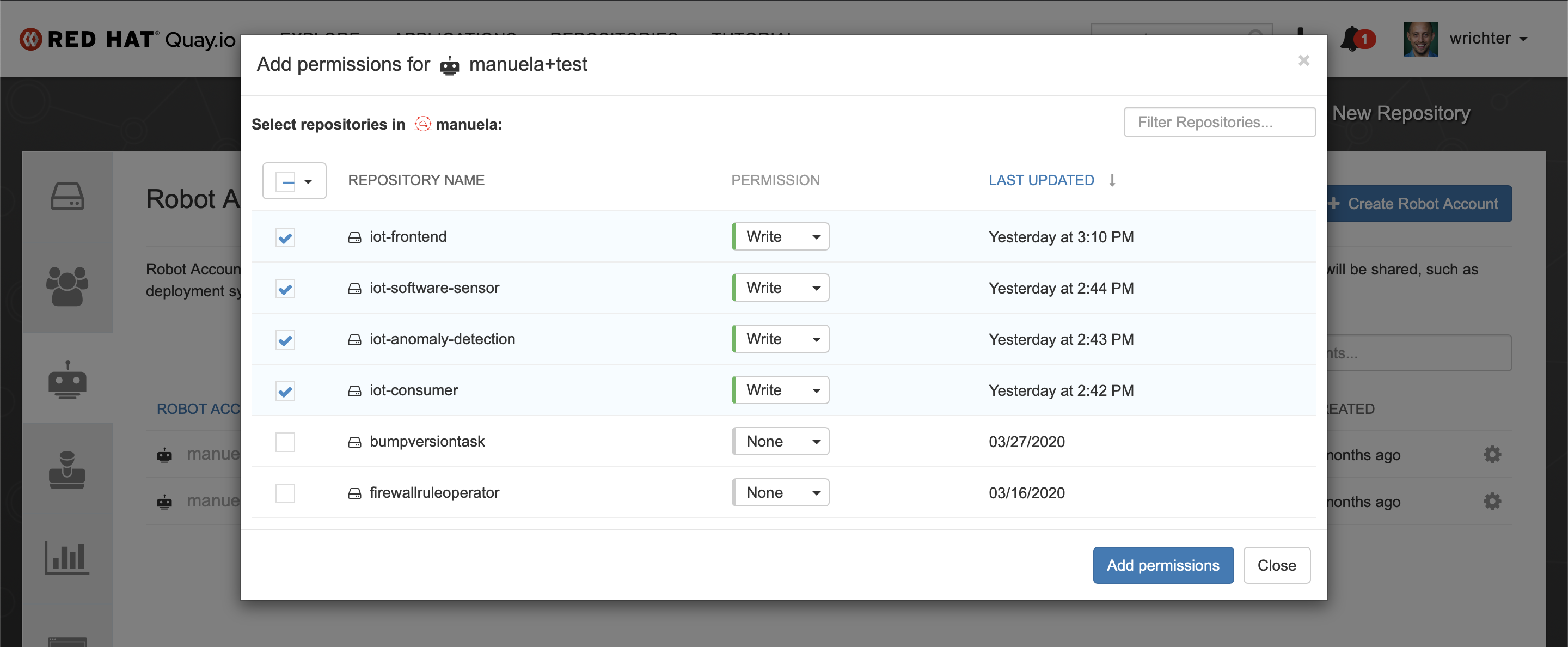
Login to https://quay.io/organization/manuela?tab=robots and note the .dockerconfigjson from the robo account “manuela-build”. You will need store it in a secret when setting up the CI and Test (Mandatory).
Virtualization environment (Optional)
If you intend to show the firewall operator, you need to run a pfSense firewall in a virtualization environment. (We currently use Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization)
Planning your installation
Some general tips to plan your installation:
- If you have clusters with different sizes, choose the largest to hold the CI/CD & Test environment.
- Code Ready Workspaces is also very resource intensive (~2 GB RAM per workspace), place it on the largest cluster as well.
- The Line Data Server environment only consists of ArgoCD and the two machine sensors which are fairly lightweight.
We suggest the following distributions:
- Two clusters:
- Cluster 1: CRW, CI/CD & Test, Central Datacenter, Factory Datacenter
- Cluster 2: Line Data Server
- Three clusters:
- Cluster 1: CRW, CI/CD & Test, Central Datacenter
- Cluster 2: Factory Datacenter
- Cluster 3: Line Data Server
- Four clusters:
- Cluster 1: CRW, CI/CD & Test
- Cluster 2: Central Datacenter
- Cluster 3: Factory Datacenter
- Cluster 4: Line Data Server
Clone the manuela repository
Clone the manuela repository. You can choose a different directory, but the subsequent docs assume it to reside in ~/manuela . Unless you want to try out the bleeding edge, it is suggested you checkout the latest manuela version tag.
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/sa-mw-dach/manuela.git
cd ~/manuela
git checkout $(git tag -l "manuela-*" | sort --version-sort | tail -n 1)
Fork and clone manuela-dev
Unless you are using the stormshift environment, create a fork of https://github.com/sa-mw-dach/manuela-dev.git to your GitHub account. Each environment should have its own set of repositories, since running the demo will alter the manuela-dev contents during the coding demo and CI/CD runs.
Then, clone the your manuela-dev repository into your home directory. This repo is the “in-storyline” repository of the dev team within the manuela demo. You can choose a different directory, but the subsequent docs assume it to reside in ~/manuela-dev .
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/<yourorg>/manuela-dev.git
If you have forked your own manuela-dev repository, you will still have references to the original manuela-dev repository in your manuela repository. These include references to operator versions via kustomization.yaml to ensure that operators deployed from content in manuela-dev and operators deployed from content in manuela are the same. This will not impact your ability to demo coding changes in manuela-dev, but if you intend to develop your fork independently and/or want to experiment with other operator versions, you need to adjust them. Search & replace “- github.com/sa-mw-dach/manuela-dev” with an adjusted link to your repo in the kustomization.yamls of your manuela repo.
Create the gitops repository
Unless you are using the stormshift environment, create a new GitOps repository. You can choose a different name, but the subsequent docs assume it to reside in ~/manuela-gitops.
Option 1: You demo stormshift and use the existing github.com/sa-mw-dach/manuela-gitops
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/sa-mw-dach/manuela-gitops.git
Option 2: You set up a new environment and use a custom GitOps repository
Create your own GitOps repo from https://github.com/sa-mw-dach/manuela-gitops-example
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/sa-mw-dach/manuela-gitops-example
mv manuela-gitops-example manuela-gitops
Publish this new directory to Github and note the GitHub URL.
git remote set-url origin https://github.com/<yourorg>/<yourrepo>.git
git push -u origin master
Adjust the GitOps repo to match your OCP clusters:
- For each (physical) cluster, create a directory in
~/manuela-gitops/deploymentbased on the sample directory. Ensure that the name of the placeholder configmap name is adjusted in each directory to match the cluster name. You can also do the same for logical clusters (i.e. linedataserver, factorydatacenter, centraldatacenter, ..) if you prefer to deploy to those. - If you intend to demonstrate the firewall operator, do the same for the network paths between the clusters.
- In the directory representing the cluster which hosts the CI/CD and Test environment, leave the manuela-tst-all symlink and delete it in the other directories. Adjust the
spec.source.repoURLvalue to match the gitops repo url. - For each (physical) cluster and for each network path between them, create an ArgoCD application in
~/manuela-gitops/metabased on the sample. Remember to adjust it’smetadata.nameto match the cluster name,spec.source.repoURLto point to the GitHub URL andspec.source.pathto point to the directory representing the cluster/networkpath in~/manuela-gitops/deployment. - Adjust the application configuration of the
line-dashboard-configmap-config.jsonin~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-tst/and~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-prodto match your environment:- Messaging URL for the machine-sensors
- Messaging URL for the line-dashboard
- Kafka bootstrap URLs for mirror-maker and S3 integration
Push the changes to GitHub:
cd ~/manuela-gitops
git add .
git commit -m "adopted to match demo env"
git push
CI and Test (Mandatory)
Create the namespaces and operators
cd ~/manuela
oc apply -k namespaces_and_operator_subscriptions/openshift-pipelines
oc apply -k namespaces_and_operator_subscriptions/manuela-ci
oc apply -k namespaces_and_operator_subscriptions/argocd
Instantiate ArgoCD
You cam also monitor the operator installation process by checking which InstallPlan and CSV are being created:
$ oc get Subscription.operators.coreos.com -n argocd -o jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{@.metadata.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installplan.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installedCSV}{'\n'}{end}"
argocd-operator install-29bkp argocd-operator.v0.0.11
Once the operator installation is complete, wait for the ArgoCD operator to be available
oc get pods -n argocd
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
argocd-operator-65dcf99d75-htjq4 1/1 Running 0 114s
Then instantiate ArgoCD and allow its service account to manage the cluster
oc apply -k infrastructure/argocd
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin -n argocd -z argocd-application-controller
Wait for the argocd resources to be created
oc get secret argocd-secret -n argocd
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
argocd-secret Opaque 2 2m12s
Check pods and routes to validate ArgoCD is running
oc get pods -n argocd
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
argocd-application-controller-7b96cb74dd-lst94 1/1 Running 0 12m
argocd-dex-server-58f5b5b44f-cfsw5 1/1 Running 0 12m
argocd-redis-868b8cb57f-dc6fl 1/1 Running 0 12m
argocd-repo-server-5bf79d67f4-hvnwx 1/1 Running 0 12m
argocd-server-888f8b6b8-scvll 1/1 Running 0 7m16s
oc get routes
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
argocd-server argocd-server-argocd.apps-crc.testing argocd-server http edge/Redirect None
Create the cluster deployment agent configuration
This also causes the manuela-tst-all testing project to be deployed via ArgocCD
oc create -n argocd -f ~/manuela-gitops/meta/argocd-<yourphysicalcluster>.yaml
Deploy the ArgoCD Cli Tool (optional)
Download the ArgoCD binary, place it under /usr/local/bin and give it execution permissions
sudo curl -L https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/download/v1.4.1/argocd-linux-amd64 -o /usr/local/bin/argocd
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/argocd
Now you should be able to use the ArgoCD WebUI and the ArgoCD Cli tool to interact with the ArgoCD Server.
Validate gitops repo via ArgoCD Web UI
Log in via OpenShift authentication (or use user: admin, password: admin) and validate that at least the cluster deployment agent configuration and manuela-tst-all is present.
To get the ArgoCD URL use:
echo https://$(oc -n argocd get route argocd-server -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')
Instantiate Tekton Pipelines
Adjust secrets
Adjust Tekton secrets to match your environments.
GitHub Secret:
cd ~/manuela-dev
export GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=changeme
sed "s/token: cmVwbGFjZW1l/token: $(echo -n $GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN|base64)/" tekton/secrets/github-example.yaml >tekton/secrets/github.yaml
cd ~/manuela-dev
export GITHUB_USER=changeme
sed "s/user: cmVwbGFjZW1l/user: $(echo -n $GITHUB_USER|base64)/" tekton/secrets/github-example.yaml >tekton/secrets/github.yaml
ArgoCD Secret:
sed "s/ARGOCD_PASSWORD:.*/ARGOCD_PASSWORD: $(oc get secret argocd-cluster -n argocd -o jsonpath='{.data.*}')/" tekton/secrets/argocd-env-secret-example.yaml >tekton/secrets/argocd-env-secret.yaml
Quay Build Secret:
export QUAY_BUILD_SECRET=ewogICJhdXRocyI6IHsKICAgICJxdWF5LmlvIjogewogICAgICAiYXV0aCI6ICJiV0Z1ZFdWc1lTdGlkV2xzWkRwSFUwczBRVGMzVXpjM1ZFRlpUMVpGVGxWVU9GUTNWRWRVUlZOYU0wSlZSRk5NUVU5VVNWWlhVVlZNUkU1TVNFSTVOVlpLTmpsQk1WTlZPVlpSTVVKTyIsCiAgICAgICJlbWFpbCI6ICIiCiAgICB9CiAgfQp9
sed "s/\.dockerconfigjson:.*/.dockerconfigjson: $QUAY_BUILD_SECRET/" tekton/secrets/quay-build-secret-example.yaml >tekton/secrets/quay-build-secret.yaml
Adjust Config Map
Adjust Tekton environment config map to match your environment. Unless you are deviating from the manuela-gitops repository structure and contents, you only need to change the values which begin with GIT_ or end with _REMOTE_IMAGE.
Instantiate Pipelines
Then instantiate the pipelines and required secrets in the manuela-ci namespace
cd ~/manuela-dev
oc project manuela-ci
oc apply -k tekton/secrets
oc apply -k tekton
Seed the git ops repo and image registries
In order to ensure that the container repositories, the manuela-tst-all namespace and the production environment have a working configuration to base demo runs on, run the seed pipeline to populate them:
oc process -n manuela-ci seed | oc create -n manuela-ci -f -
Wait for the pipeline to complete successfully.
Factory Datacenter & Line Data Server (Mandatory)
For the individual physical clusters representing the factory datacenter and the line data server, ensure that ArgoCD is deployed and allowed to manage the cluster. If you have already done this as part of the setup of another logical environment, you may skip this step.
cd ~/manuela
oc apply -k namespaces_and_operator_subscriptions/argocd
oc apply -k infrastructure/argocd
Ensure that the deployment agent configuration for the respective cluster is present:
oc apply -n argocd -f ~/manuela-gitops/meta/argocd-<yourphysicalcluster>
Refer to Validate GitOps repository via ArgoCD Web UI to validate the ArgoCD setup.
Optional extensions
Development (Optional)
You only need to install this if you intend to develop the demo application. This will provide you with an AMQ Broker and configurations to build and deploy the container images in the iotdemo namespace.
Adjust the ~/manuela-dev/components/iot-frontend/manifests/iot-frontend-configmap-config.json to the target environment (Note: the software sensor components uses the internal service name to reach the AMQ broker, and therefore do not need adjustments):
{
- "websocketHost": "http://iot-consumer-iotdemo.apps.ocp4.stormshift.coe.muc.redhat.com",
+ "websocketHost": "http://iot-consumer-iotdemo.apps.ocp3.stormshift.coe.muc.redhat.com",
"websocketPath": "/api/service-web/socket",
"SERVER_TIMEOUT": 20000
}
Instantiate the development environment.
cd ~/manuela
oc apply -k namespaces_and_operator_subscriptions/iotdemo
Wait for the operators to be installed
$ oc get Subscription.operators.coreos.com -n iotdemo -o jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{@.metadata.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installplan.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installedCSV}{'\n'}{end}"
amq-broker install-26b9s amq-broker-operator.v0.15.0
amq-streams install-26b9s amqstreams.v1.5.2
red-hat-camel-k install-26b9s red-hat-camel-k-operator.v1.0.0
seldon-operator install-p8t7g seldon-operator.v1.2.1
Then instantiate the development components. Note: this will kick off a build of all components which will take several minutes.
oc project iotdemo
cd ~/manuela-dev
oc apply -k components
CodeReady Workspaces (Optional)
If you want to demo the code change story line using CodeReady Workspaces instead of a local dev environment (or a simple git commit/push), you need to setup Code Ready Workspaces.
This provides CodeReady Workspaces as alternative development environment
cd ~/manuela
oc apply -k namespaces_and_operator_subscriptions/manuela-crw
This will create the following:
- Create a new project manuela-crw in the current logged in OCP
- Create an OperatorGroup CR to make the OLM aware of an operator in this namespace
- Create an CRW Operator Subscription from the latest stable channel -> installs the CRW operator in the namespace manuela-crw
Wait for the operator installation to complete:
oc get Subscription.operators.coreos.com -n manuela-crw -o jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{@.metadata.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installplan.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installedCSV}{'\n'}{end}"
Then instantiate the CRW resources:
oc apply -k infrastructure/crw
This will create an actual CheCluster in the namespace manuela-crw with following custom properties
customCheProperties:
CHE_LIMITS_USER_WORKSPACES_RUN_COUNT: '10'
CHE_LIMITS_WORKSPACE_IDLE_TIMEOUT: '-1'
CRW should be available after about 3-5 minutes after the previous installation steps.
- Check and wait that the pods are online:
oc project manuela-crw oc get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE codeready-7898fc5f74-qz7bk 1/1 Running 0 4m59s codeready-operator-679f5fbd6b-ldsbq 1/1 Running 0 8m2s devfile-registry-58cbd6787f-zdfhb 1/1 Running 0 6m11s keycloak-567744bfd6-dx2hs 1/1 Running 0 7m15s plugin-registry-6974f58d59-vh5hc 1/1 Running 0 5m43s postgres-55ccbdccb-cnnbc 1/1 Running 0 7m48s - Check that you can login. Look for the route with the name codeready:
echo https://$(oc -n manuela-crw get route codeready -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')Point your browser to the URL and use your OpenShift Account (OpenShift OAuth is enabled) to login.
Bookmark that URL !
Management Cluster(s) and Firewall VM(s) (Optional)
ArgoCD deployment agent configuration
Ensure that ArgoCD is running on and able to manage the management cluster(s). See the instructions for the Factory Datacenter & Line Data Server for details. Create the deployment agent configuration:
cd ~/manuela-gitops/meta/
oc apply -n argocd -f argocd-nwpath-<cluster1>-<cluster2>.yaml
Set Up pfSense Firewall VM
Download pfSense ISO (CD/DVD) image from https://www.pfsense.org/download/ and upload the ISO image to your virtualization environment, e.g. https://rhev.stormshift.coe.muc.redhat.com/.
Create 2 new VMs (mpfuetzn-ocp3-pfsense and mpfuetzn-ocp4-pfsense) as follows:
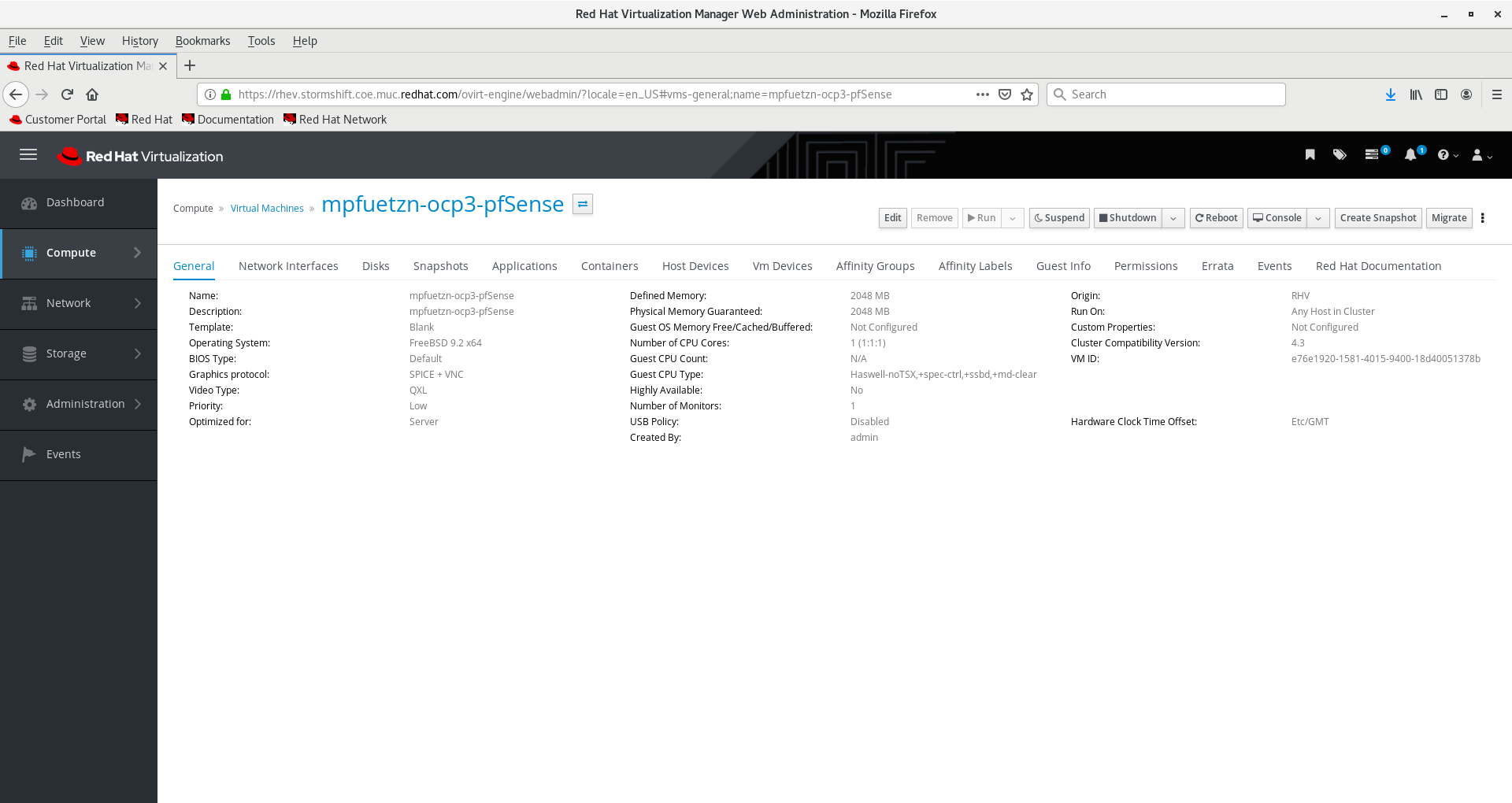
Add Network Interfaces. Nic1 (LAN) needs to be in a routable network reachable from the management cluster, such as ovirtmgmt for RHV. For example:
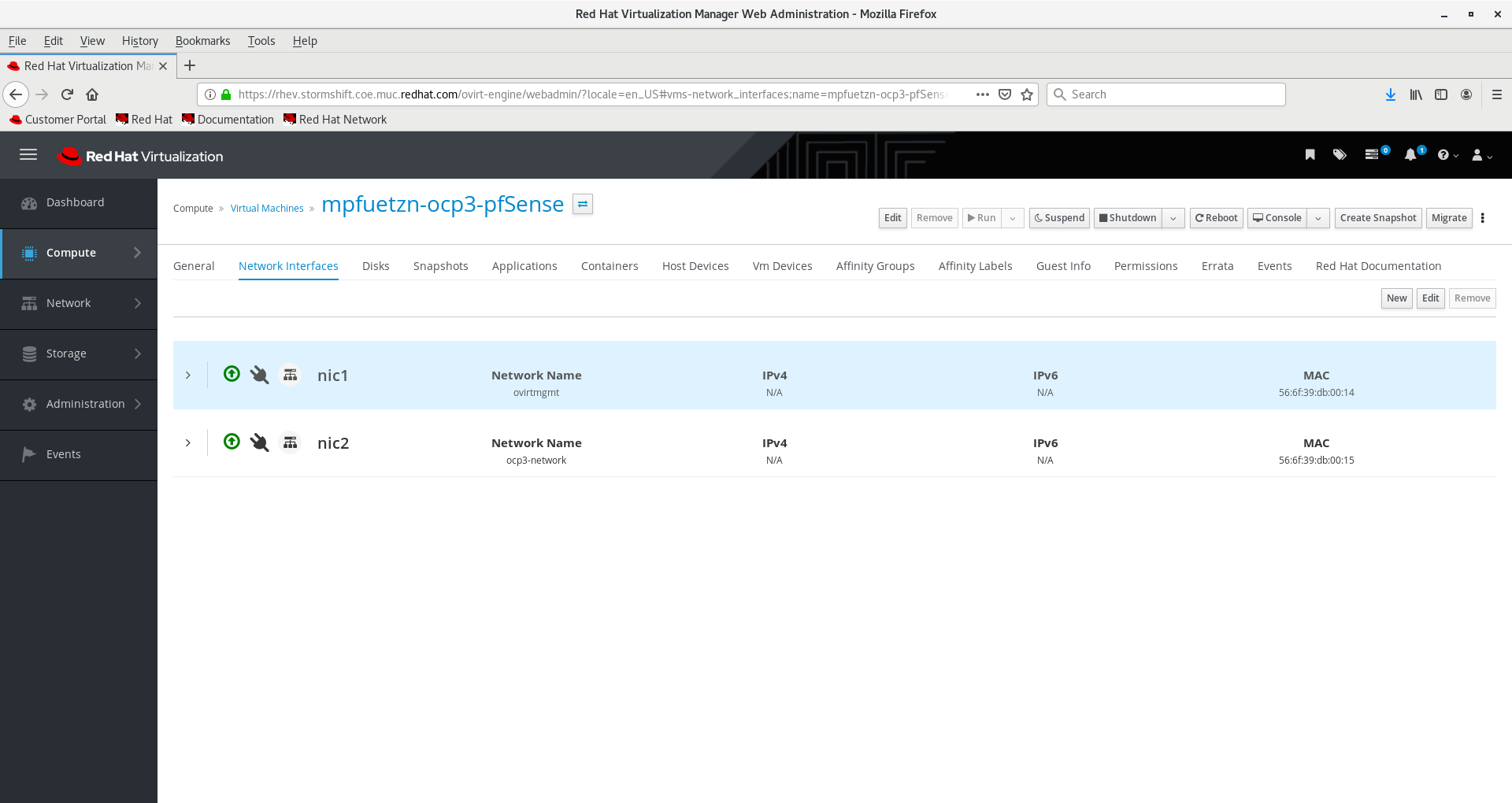
(replace ocp3 for ocp4 in the second machine!)
Attach the CD-ISO image to the VM to boot from for the first time
After install, and after the first reboot (do not forget to remove the CD-ISO Image!) configure as follows:
- NO VLANS
- WAN interface is vtnet1 (aka the ocp3-network)
- LAN interface is vtnet0 (aka the ovirtmgt network)
- LAN now also needs a fix IP and a router: ocp3 has 10.32.111.165/20 as IP and 10.32.111.254 as router, ocp4 has 10.32.111.166/20 as ip and the same router
- WAN gets its IP via DHCP in the range of 172.16.10.???/24
Default password for the appliances is admin/pfsense
Configure rules
The default rules configured might not be suitable to the story being told, i.e. a locked down environment. Per default, all IP4/6 traffic is allowed from LAN to WAN.
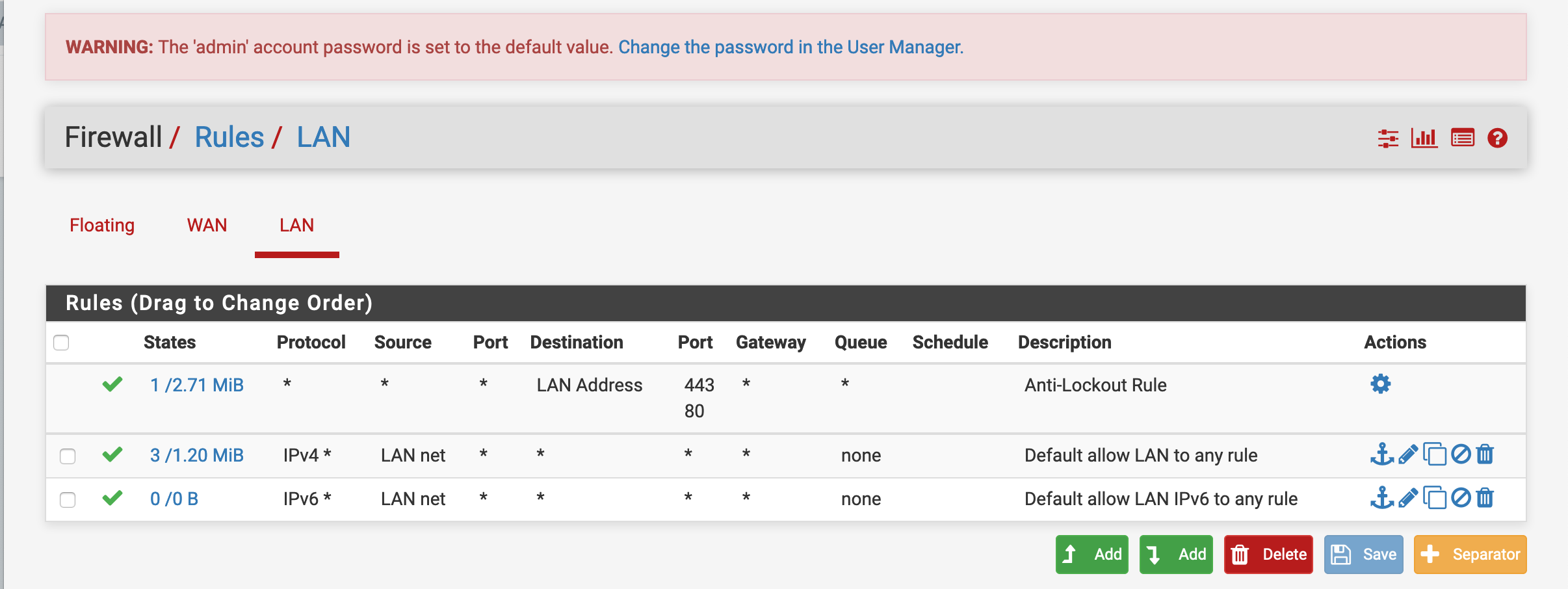
Replace these rules with a “Default deny all” rule blocking IP4+6.
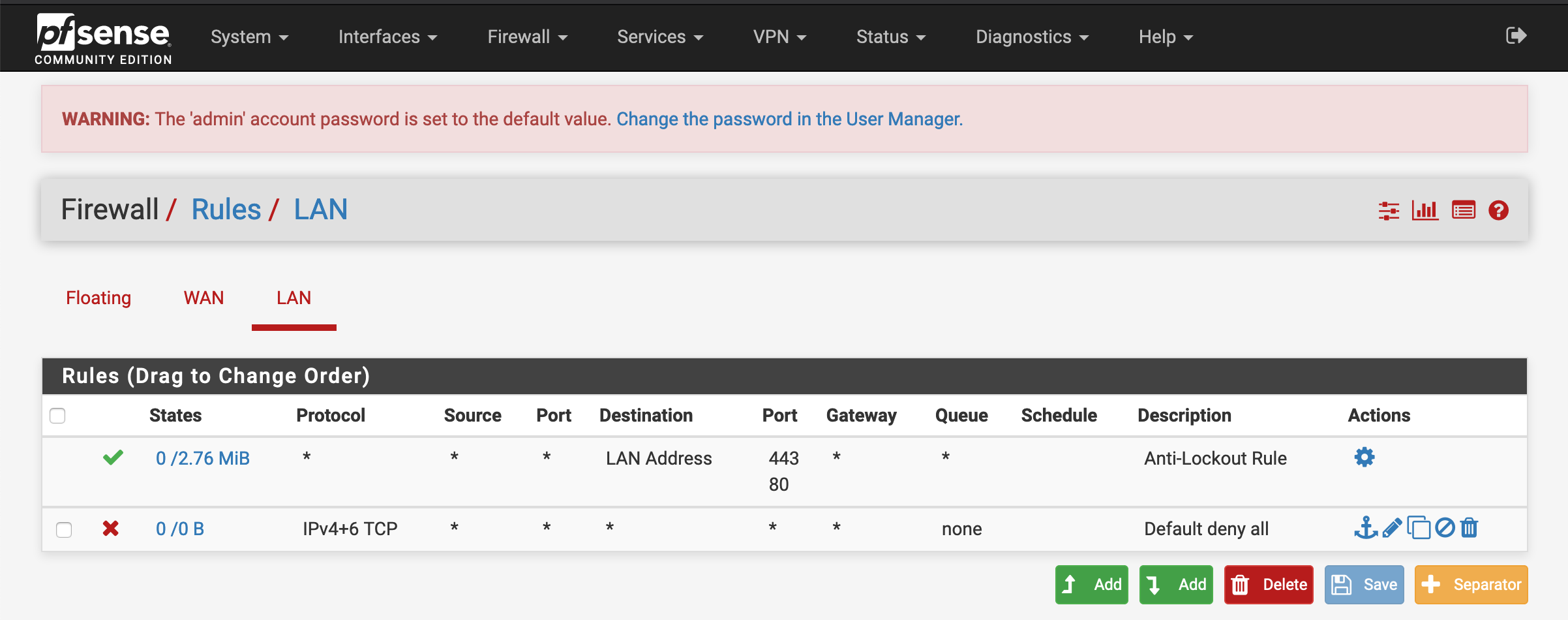
Set root ssh key
For the demo ssh-access needs to additionally be enabled and keys generated, because the operator needs to be able to access the pfsense appliance via Ansible. Generate a keypair which will be used to access the demo
$ ssh-keygen -f keypair
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in keypair.
Your public key has been saved in keypair.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:e2hUI5thMlfnCCpLW3gS1ClipfGywPYY391+SrO8xx4 vagrant@ibm-p8-kvm-03-guest-02.virt.pnr.lab.eng.rdu2.redhat.com
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| .o+. .. . . |
|. o+.oo. o + |
|.=o.*.* = + . |
|..=+.B.=.* . |
| ..oo. .S. |
| ..o |
| ++oE |
| .o.=o. |
| =+. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
$ cat keypair.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCw5CP4Sj1qp6cLb2Bp6grN59qOUuBrOfz7mc12848TP+PyLtS8KL6GBpb0ySOzEMIJdxhiZNHLiSLzh7mtHH0YXTdErdjD2hK9SOt9OmJrys8po9BLhVvacdRDS0l2BFyxG7gaCU92ZmTJHKtLi2jpOLMFNXl5oSva0u5WL+iYQJhgBCezxCSKhUquxLL9Ua9NThkhb064xzm7Vw0Qx53VY89O6dOX7MFeLM19YT1jfLDJ0CGWNju3dyFbQNNmn/ZquP91DFeV9mTS2lP/H+bd20osDScEzE+c3zeDsP8UmLbOhBsQs6kRXLos58Ag3vjCommULfPnHvTFbgVKbwnh [vagrant@ibm-p8-kvm-03-guest-02.virt.pnr.lab.eng.rdu2.redhat.com](mailto:vagrant@ibm-p8-kvm-03-guest-02.virt.pnr.lab.eng.rdu2.redhat.com)
Log into pfsense firewall with default username/pw
$ ssh root@10.32.111.165
The authenticity of host '10.32.111.165 (10.32.111.165)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:ZoXQTnMit+NaHMvQbfTPT3/ztn+xkUB7BrVSptxjBvg.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '10.32.111.165' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
Password for root@pfSense.localdomain:
pfSense - Netgate Device ID: 445f648407f99eee6675
*** Welcome to pfSense 2.4.4-RELEASE-p3 (amd64) on pfSense ***
WAN (wan) -> vtnet1 -> v4/DHCP4: 172.16.10.102/24
LAN (lan) -> vtnet0 -> v4: 10.32.111.165/20
1) Logout (SSH only) 9) pfTop
2) Assign Interfaces 10) Filter Logs
3) Set interface(s) IP address 11) Restart webConfigurator
4) Reset webConfigurator password 12) PHP shell + pfSense tools
5) Reset to factory defaults 13) Update from console
6) Reboot system 14) Disable Secure Shell (sshd)
7) Halt system 15) Restore recent configuration
8) Ping host 16) Restart PHP-FPM
9) Shell
Enter an option: **8**
[2.4.4-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root: cat >>.ssh/authorized_keys
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCw5CP4Sj1qp6cLb2Bp6grN59qOUuBrOfz7mc12848TP+PyLtS8KL6GBpb0ySOzEMIJdxhiZNHLiSLzh7mtHH0YXTdErdjD2hK9SOt9OmJrys8po9BLhVvacdRDS0l2BFyxG7gaCU92ZmTJHKtLi2jpOLMFNXl5oSva0u5WL+iYQJhgBCezxCSKhUquxLL9Ua9NThkhb064xzm7Vw0Qx53VY89O6dOX7MFeLM19YT1jfLDJ0CGWNju3dyFbQNNmn/ZquP91DFeV9mTS2lP/H+bd20osDScEzE+c3zeDsP8UmLbOhBsQs6kRXLos58Ag3vjCommULfPnHvTFbgVKbwnh vagrant@ibm-p8-kvm-03-guest-02.virt.pnr.lab.eng.rdu2.redhat.com**
[2.4.4-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root: exit
exit
pfSense - Netgate Device ID: 445f648407f99eee6675
*** Welcome to pfSense 2.4.4-RELEASE-p3 (amd64) on pfSense ***
WAN (wan) -> vtnet1 -> v4/DHCP4: 172.16.10.102/24
LAN (lan) -> vtnet0 -> v4: 10.32.111.165/20
0) Logout (SSH only) 9) pfTop
1) Assign Interfaces 10) Filter Logs
2) Set interface(s) IP address 11) Restart webConfigurator
3) Reset webConfigurator password 12) PHP shell + pfSense tools
4) Reset to factory defaults 13) Update from console
5) Reboot system 14) Disable Secure Shell (sshd)
6) Halt system 15) Restore recent configuration
7) Ping host 16) Restart PHP-FPM
8) Shell
Enter an option: **^D**
Connection to 10.32.111.165 closed.
Install & Prepare the firewall operator (once per firewall instance)
Each firewall instance is represented by a namespace in the management cluster. These namespaces have to match the namespaces in the ~/manuela-gitops/meta/argocd-nwpath-<cluster1>-<cluster2>.yaml files. Create the namespace via oc command. Replace manuela-networkpathoperator with your chosen namespace in the subsequent command examples
oc new-project manuela-networkpathoperator
Prepare a secret for the operator deployment. Adjust hostname, username, SSH private key for firewall access as created before
cd ~/manuela-dev/networkpathoperator/firewallrule/deploy
cp firewall-inventory-secret-example.yaml firewall-inventory-secret.yaml
vi firewall-inventory-secret.yaml
Deploy the operator to the new namespace
cd ~/manuela-dev
oc project manuela-networkpathoperator
oc apply -n manuela-networkpathoperator -f networkpathoperator/firewallrule/deploy/firewall-inventory-secret.yaml
oc apply -k networkpathoperator/firewallrule/deploy
Test the sample firewall rule
oc apply -n manuela-networkpathoperator -f deploy/crds/manuela.redhat.com_v1alpha1_firewallrule_cr.yaml
Validate that the firewall rule in deploy/crds/manuela.redhat.com_v1alpha1_firewallrule_cr.yaml is created appropriately in the firewall (via firewall UI). Then remove the firewall rule
oc delete -n manuela-networkpathoperator -f deploy/crds/manuela.redhat.com_v1alpha1_firewallrule_cr.yaml
Validate that the firewall rule in deploy/crds/manuela.redhat.com_v1alpha1_firewallrule_cr.yaml is removed appropriately from the firewall (via firewall UI).
Machine Learning based Anomaly Detection and Alerting (Optional)
Machine Learning based alerting is not enabled by default in the iotdemo and stormshift (test & prod) environment. The following section describes how to enable and disable the Machine Learning based Anomaly Detection and Alerting for iotdemo and stormshift (test & prod) environment.
Note, the steps how to deploy an OpenDataHub with JupyterHub is described in the Demo Preparation
Let’s look at the Stormshift test & prod first
Please clone the manuela-gitops and manuela repos into your home directory. You can choose a different directory, but the subsequent docs assume it to reside in ~/manuela-gitops and ~/manuela .
Bootstrap and configure Anomaly Detection Service in manuela-tst-all
login into ocp3 as admin or with admin privileges and switch to the manuela-tst-all project
oc login -u XXX -p XXXX --server=https://api.ocp3.stormshift.coe.muc.redhat.com:6443
oc project manuela-tst-all
Validate Seldon Operator
Check if the SeldonCore Operator is deployed:
oc get csv -n manuela-tst-all | grep -i seldon
Expected results:
seldon-operator.v1.2.0 Seldon Operator 1.2.0 Succeeded
You can also monitor the operator installation if it is still runnign with
$ oc get Subscription.operators.coreos.com -n manuela-ml-workspace -o jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{@.metadata.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installplan.name}{'\t'}{@.status.installedCSV}{'\n'}{end}"
seldon-operator install-4p5h7 seldon-operator.v1.2.1
Build iot-anomaly-detection container by running the pipeline
Check if the anomaly-detection image stream already exists:
oc get is anomaly-detection -n manuela-tst-all
Expected results:
NAME IMAGE REPOSITORY TAGS UPDATED
anomaly-detection default-route-openshift-image-registry.apps.ocp3.stormshift.coe.muc.redhat.com/manuela-tst-all/anomaly-detection 0.0.1-7 8 minutes ago
If not, run the pipeline to build the anomaly-detection image.
Enable Seldon service
Edit ~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-tst/kustomization.yaml
and uncomment the line ../../templates/manuela-openshift/anomaly-detection
For example …
...
# Comment out the following line if you don't want to run anomaly-detection (ODH)
- ../../templates/manuela-openshift/anomaly-detection
...
Push changes to master. ArgoCD will pickup the change.
Test the anomaly detection service
curl -k -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"data": { "ndarray": [[16.1, 15.40, 15.32, 13.47, 17.70]]}}' http://$(oc get route anomaly-detection -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}' -n manuela-tst-all)/api/v1.0/predictions
Expexted result:
{"data":{"names":[],"ndarray":[1]},"meta":{}}
Enable the vibration alert and vibration anomaly detection in the messaging-configmap
Update the messaging config map:
In ~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-tst/messaging/messaging-configmap.properties set
VIBRATION_ALERT_ENABLED=true
VIBRATION_ANOMALY_ENABLED=true
cd ~/manuela-gitops/
sed -i "s|VIBRATION_ANOMALY_ENABLED.*|VIBRATION_ANOMALY_ENABLED=true|" config/instances/manuela-tst/messaging-configmap.properties
sed -i "s|VIBRATION_ALERT_ENABLED.*|VIBRATION_ALERT_ENABLED=true|" config/instances/manuela-tst/messaging-configmap.properties
git add .
git commit -m "enable vibration anomaly alert"
git push
Push the changes to github and wait that ArgoCD picks up the change. This should automatically redeploy the pods since the generated configmap name changed.
Check the messaging log to see if Anomaly web service is called.
oc logs -f deployment/messaging -n manuela-tst-all
You can also check the log of the anomaly-detection-predictor:
oc logs -f anomaly-detection-predictor-XXXXX -c anomaly-detection -n manuela-tst-all
Expected log:
Anomaly detection for: floor-1-line-1-extruder-1pump-2, Val: 10.448725266151287
*AD* ID: floor-1-line-1-extruder-1pump-2, Val: 10.448725266151287
vibration alert!!!
Expected log:
2020-04-30 08:49:08,702 - werkzeug:_log:113 - INFO: 127.0.0.1 - - [30/Apr/2020 08:49:08] "POST /predict HTTP/1.1" 200 -
Predict features: [[17.45270494 16.18148444 15.33149548 37.02017565 14.3998071 ]]
Prediction: [0]
2020-04-30 08:49:08,784 - werkzeug:_log:113 - INFO: 127.0.0.1 - - [30/Apr/2020 08:49:08] "POST /predict HTTP/1.1" 200 -
Predict features: [[10.44872527 11.30054612 13.24766808 14.47263542 40.36102793]]
Prediction: [1]
Bootstrap and configure Anomaly Detection Service in production (manuela-stormshift-odh)
Prerequitsites:
- Anomaly Detection Service is deployed in manuela-tst-all
- Pipeline iot-anomaly-detection run successfully
Enable Seldon service
Let’s assume you cloned the manuela-gitops repository already.
Edit ~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-stormshift/messaging/kustomization.yaml
vi ~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-stormshift/messaging/kustomization.yaml
and uncomment - ../../../templates/manuela-openshift-prod/anomaly-detection
...
# Comment/uncomment following line to disable/enable anomaly-detection deployment
- ../../../templates/manuela-openshift-prod/anomaly-detection
...
Push changes
git add ~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-stormshift/messaging/kustomization.yaml
git commit -m "enable anomaly-detection"
git push
Enable Vibration Alert and Vibration Anomaly detection in messaging-configmap of manuela-stormshift
Update the messaging config map:
Edit ~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-stormshift/messaging/messaging-configmap.properties and set the following paramters:
...
VIBRATION_ALERT_ENABLED=true
VIBRATION_ANOMALY_ENABLED=true
NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED=0
...
Push the changes to github and wait that ArgoCD picks up the change.
Push changes
git add ~/manuela-gitops/config/instances/manuela-stormshift/messaging/messaging-configmap.properties
git commit -m "enable anomaly detection alerts"
git push
Check the messaging log to see if Anomaly web service is called (see above).
Configure Anomaly Detection Service in iotdemo
Edit ~/manuela-dev/components/kustomization.yaml and uncomment - iot-anomaly-detection/manifests
# Open data hub is optional
- iot-anomaly-detection/manifests
Deploy or redeploy iotdemo. See Development (Optional)